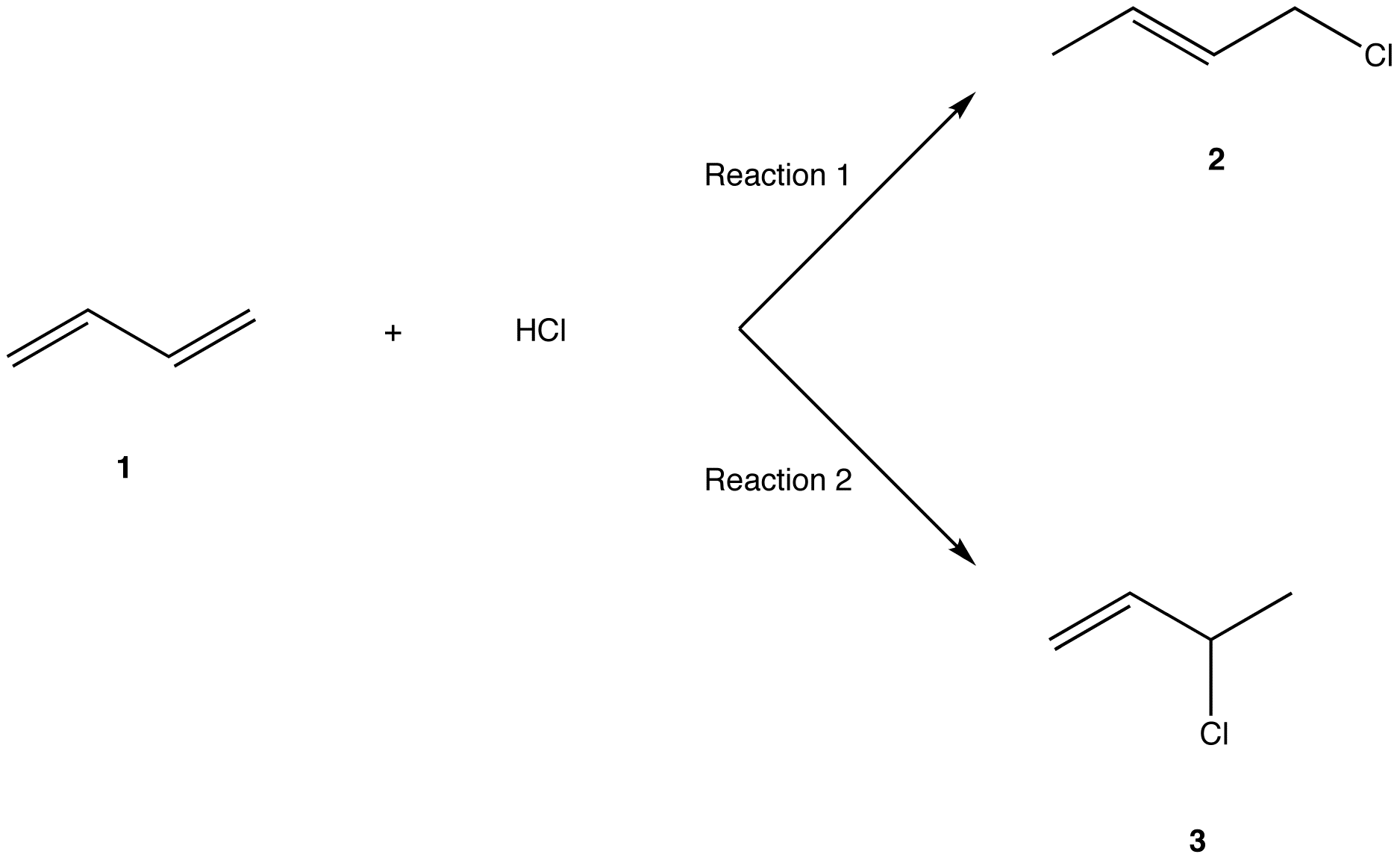
1 2 And 1 4 Addition Products
Did you start by considering the first step of.
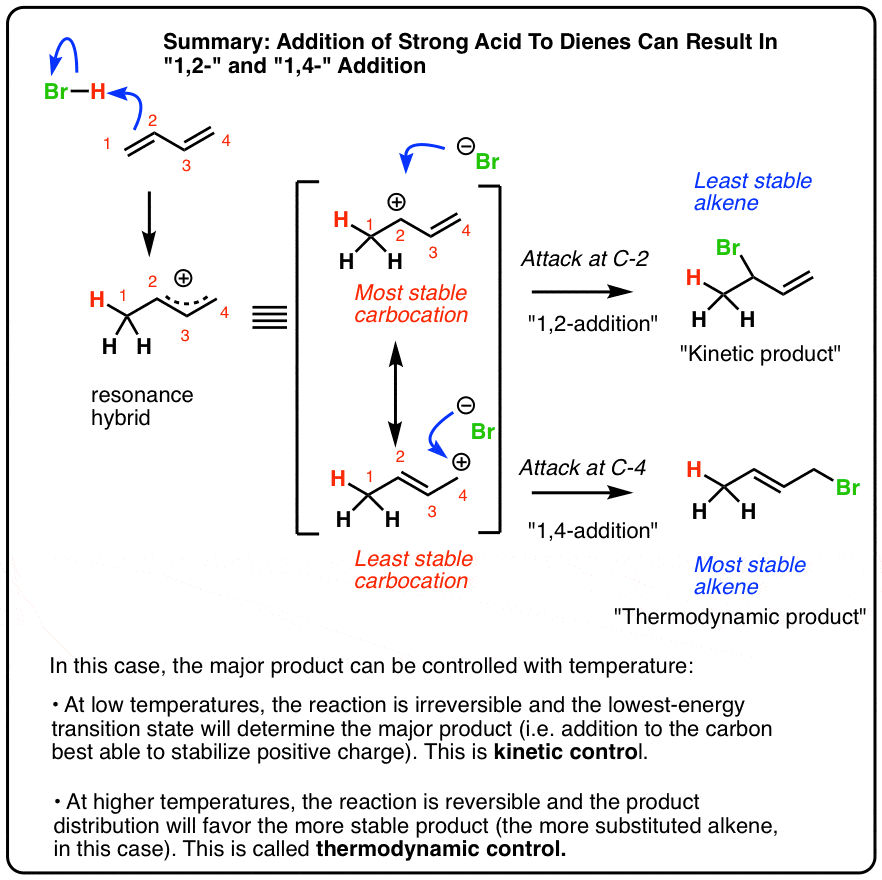
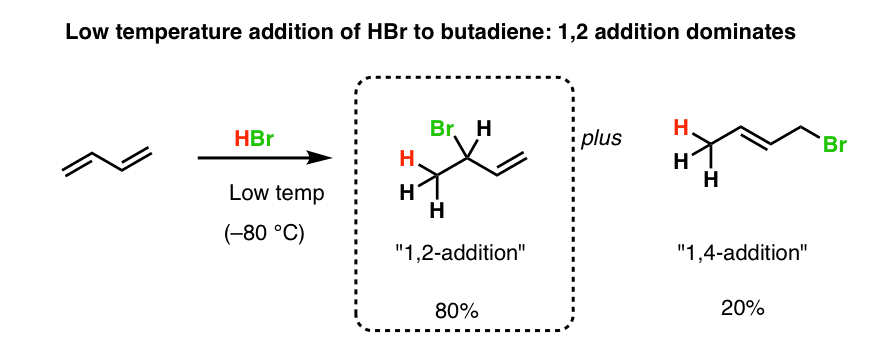
1 2 and 1 4 addition products. Hence reaction 1 is called 1 4 addition and its product 2 1 4 adduct. I came up with the following but i m not sure if they re correct. Attack at c 2 provides the 1 2 product. For example the addition of hydrogen bromide to 1 3 butadiene at temperatures below zero leads mainly to the 1 2 addition product while addition reactions run at temperatures above 50 c with these chemicals produces mainly the 1 4 addition product.
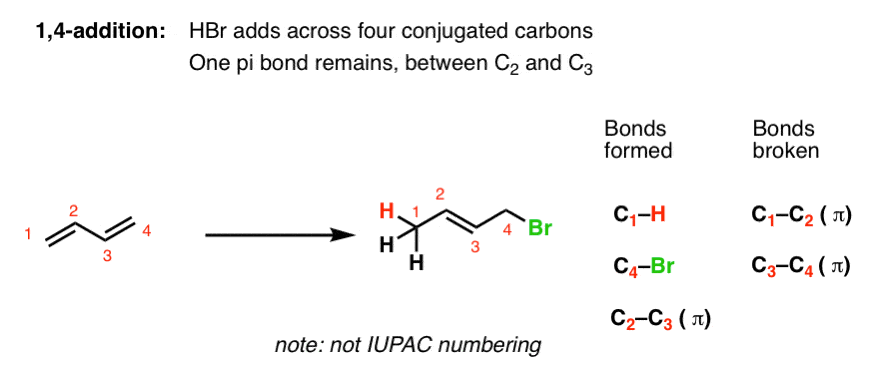
Since 1 2 additions to the carbonyl group are fast we would expect to find a predominance of 1 2 products from these reactions. 1 4 addition is an electrophilic addition reaction of conjugate dienes. This is the basis of what we now call kinetic and thermodynamic control. Attack of the nucleophile can occur at two different positions.
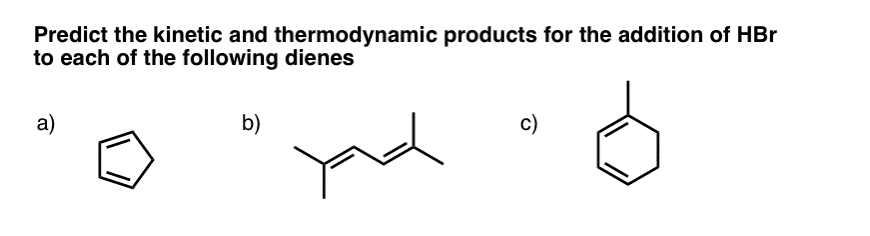
Question draw the major 1 2 and 1 4 addition products obtained in the reaction shown. Assume that both are derived from the most stable carbocation intermediate. He suggests the general idea that the 1 2 and 1 4 addition products are in equilibrium and that the 1 2 product can reverse reaction and form the 1 4 product. Also i m having trouble naming the products i came up with.
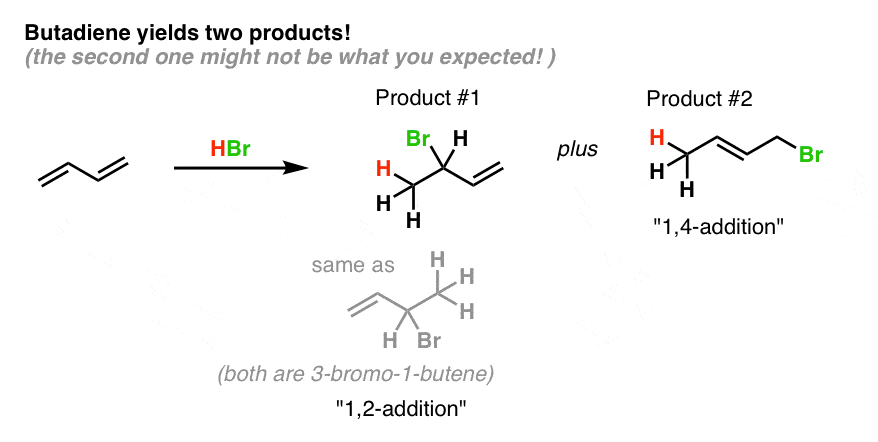
In reaction 1 the net reaction is addition of a hydrogen atom to c 1 and a chlorine atom to c 4 in 1. The expected addition product from reactions of this kind is the result of 1 2 addition i e. 1 2 and 1 4 addition products 7. Ch br 2chbrchch2 would this now be 3 4 tribromo 1 butene for 1 4 addition.
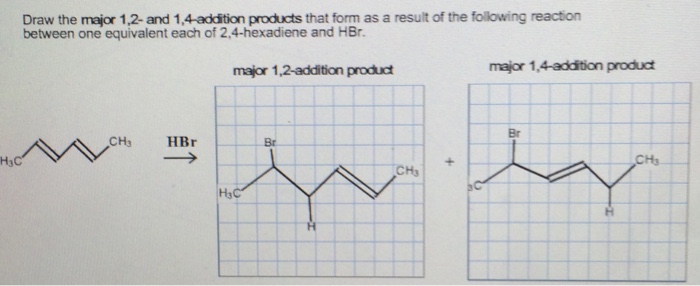
Question draw the major 1 2 and 1 4 addition products that form as a result of the following reaction between one equivalent each of 2 4 hexadiene and hbr. 1 2 and 1 4 products in addition of br 2 to butadiene. Whether more 1 2 addition or 1 4 addition product is created depends largely on the temperature at which the reaction is run. Draw the 1 2 and 1 4 addition products for the following reaction and provide a complete and detailed mechanism that accounts for their formation.
Attack at c 4 provides the 1 4 product. When a dihalogen such as br 2 is added to a diene such as butadiene a bromonium ion intermediate will form on one of the double bonds. This means the competition between 1 2 and 1 4 addition is under thermodynamic control. Bonding at the terminal carbon atoms of a conjugated diene with a shift of the remaining double bond to the 2 3 location these numbers refer to the four carbons of the conjugated diene and are not.
Of course there are two products the markovnikov and the anti markovnikov. Bonding to the adjacent carbons of a double bond the unexpected product comes from 1 4 addition i e. Two electrophilic addition reactions could occur between 1 3 butadiene 1 and hydrogen chloride.